ID Artifacts
This page contains artifacts, aka examples, of different projects done throughout my instructional design studies at George Mason University. Also included are artifacts from my time as the Director of Library Services at Virginia International University, including Conference Presentations, Outreach & Marketing, and Reports & Studies.
Instructional Software Examples
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
Keywords: Scripting, cognitive load, online instruction, emerging technologies.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Foundations; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development.
What I Learned
As many learned during the COVID-19 pandemic, online learning is different than face-to-face instruction. In each example, I use a blend of objectivist and constructivist methodologies. The modules are in a objectivist design of the teacher leading the instruction with the instruction following my lead throughout with a selection of the materials mixing video and reading. The scenarios are authentic with assessment being short quizzes and short written response. In the end of both the Articulate 360 and Adobe Captivate examples, the learner is to create their own plan based on the online instruction. Here, the instruction and assessment are constructivist with a problem-based learning model with the learner creating their own plan based on the online materials and modules.
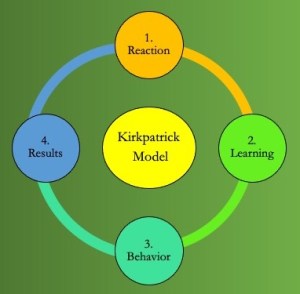
EDIT 590 Evaluating Academic Information Literacy Using the Kirkpatrick Model as an Evidence-Based Framework
In this education research class, I prepared a study proposal per the class assignment. My work proposed a mixed-methods study on using the Kirkpatrick Model as a framework in measuring student success in applying information literacy instruction. Using the Kirkpatrick Model, library management working with other campus stakeholders could align university strategic objectives to instruction demonstrating evidenced-based changes in student performance and acceptance of the training. I have found the Kirkpatrick Model simple in its design framework, yet challenging in making the evaluator pursue evidenced-based data in the pursuit that training worked.
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
Keywords: The Kirkpatrick Model, education research, backwards design, evidenced-based assessment, information literacy.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Foundations; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development; Evaluation and Implementation.

English as a Second Language Information Literacy Lesson Plans by Reading level
During my tenure as Director of Library Services, I collaborated with our librarian and faculty to create these lesson plans. Under my leadership, our team took a fifteen minutes one-shot library instruction plan and transformed it into eight lesson plans based on ESL students’ reading level. The lesson plans utilized Lev Vgotsky’s scaffolding theory as well as self-directed learning. Based on comfort level, students could work alone or in a group to complete the assignment. A librarian would be nearby to provide instructions or scaffold as needed.
Keywords: Curriculum Development, Information Literacy, Needs Assessment, Self-directed learning, Scaffolding.
IBSTPI Competencies: Planning and Analysis; Design and Development; Evaluation and Implementation.
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
What I learned
Our ESL students struggled to use a catalog and find books. In order to gain empathy, the librarians consulted ESL instructors to understand reading development through the eight levels of the program. We decided to separate ESL books into its own section and regrouped the books by category and title instead of the classification system. With instruction, we redesigned the lessons to be learner-centered with allowing the students to work alone or in pairs. Instructors would move to role of facilitator with providing assistance as needed. This scaffolding design improved students’ application of skills and learning. Mostly, I learned through creativity and a willingness to surrender control that students learned more and demonstrated their skills.

EDIT 706 Business Case Cheaper alternatives to current textbooks at Virginia International University
The purpose of the Business Case was to identify a learning challenge that has negative impact on the performance on an organization. The assignment was to create a written rationale with observable and measurable benefits, considering both the financial and human resources. In this work, I was to identify: the nature of the problem; alternatives to consider with assumptions and risks; financial metrics and measures; and an evaluation plan. My recommendation had to rely on evidenced-based research and establish key point indicators. My business case addressed the high cost of textbooks and its impact on student retention and achievement.
Keywords: Business Case; Cost Management Process; Evidence-based Research; Metrics; Organizational Culture; Project Management
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Foundations; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development; Evaluation and Implementation; and Management.
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
What I learned
This business case is the best example of my writing and provides solid evidence-based research to support my proposal. Using quantitative data from two different universities, my case provided proof of increased grades, retention, and resource use when students utilize free or inexpensive textbooks comparing classes where students purchased works or not. From here, I had to provide three scenarios for implementing a plan, including do nothing, a middle of the road option, and full implementation. My recommendation was the latter and involved 14 months for faculty with measurable key performance points. The plan involved some training from outside facilitators and a campus review of all materials to provide quality resources at little or no cost. Our competitors, where many students transferred, offered education without expensive materials. Through the preparation, I learned that having solid, evidenced-based research helps in making the argument. An instructional designer must make a thorough project plan for implementation and estimate the financial and human capital necessary. Furthermore, the designer must have measurable goals, be willing to take risks, and report the project’s progress to upper management. I believe this course prepared me the best for making formal, data-driven proposals in an organization.

COS 600 Design Thinking Project Addressing Sustainable Goal of Education during the COVID-19
This paper explores why faculty were not prepared to teach online and how Mason can engage students better in the future. Through design thinking, three graduate students applied research towards solving this problem. The result was attainable, measurable, and realistic S.M.A.R.T. goals. For faculty, the plan calls for the creation of a Community of Practice, improved resources, and both financial as well as professional development incentives. The plan allows the schools to integrate training without changes to the employee handbook or other institutional procedures.
Keywords: Community of Practice; Design Thinking; Empathy Mapping; Gaant Chart; Root Cause Analysis; and Sustainable Goals 2030.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Competencies; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development; Evaluation and Implementation; and Management.
Click on picture for a link to PowerPoint. For final paper, click here.
What I learned
As spring term 2020 progressed, the pandemic grew of greater attention and concern. The purpose of the class was to learn different problem solving techniques and technologies for S.T.E.A.M. leadership. Dr. Seshaiyer used the Sustainable Goals 2030 as our focus in problem solving. Our group chose education and focused on the disruption of education at George Mason University, which had moved to online-only courses during the final six weeks of the semester. Through using the steps of design thinking, our group created a plan. In the first step we used empathy maps to learn how students were handling the transition. In addition, we examined published student reactions. Affinity mapping assisted us in categorizing responses and then, we used root-cause analysis with the 5 Whys. Using a brain-write activity, we created solutions and developed our prototype plan. Following the design thinking process made the creation of a prototype easier. The key here is learning the user experience. Anytime the group reached an impasse, we reviewed our empathy mapping . This notion has had the greatest impact on me in instructional design.
EDIT 611 Design Thinking E-Learning Module for GMU Faculty
The purpose of this assignment was to create a thirty minute online training module. My focus was to teach faculty about design thinking and have them apply the learning in the final step by creating a lesson plan. This online module followed an objectivist approach meaning the teacher controlled the learning throughout. This employed “hard scaffolding” with resources provided in the learning module and the learner could reach a facilitator through email if further assistance was necessary.
Keywords: Continuity principle; Design Thinking; Motivation; E-learning; and Objectivism.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Competencies; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development.
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
What I Learned
Online learning is very different from face-to-face instruction. Taking this course while simultaneously taking EDIT 732 with its emphasis on constructivism created a design dilemma. While wanting to create a student-centered design with an ill-situated problem, the approach became the best way to teach about design thinking while focusing on the lowest three levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. In the first seven modules, the faculty were learning how to remember, understand, and apply. In the final step, faculty were to create a lesson plan. I learned to use a variety of resources to motivate and engage the learner. In several modules, I used short videos to explain concepts. In other modules, I provided short reading. In every module was the opportunity to comment on the blog on what one learned and the learner could read other’s responses. In the end, I created an E-learning module that engaged the learner and offered motivation to learn through professional development incentives.
EDIT 526 Accessible Website
Creating a website accessible for people with disabilities involves many design challenges. The process involved a lot of trial and error testing with screen readers and accessibility software. This assignment was to make an accessible website on any topic. Click on picture on the left for project description and accessibility test results.
Keywords: American with Disabilities Act; CSS; HTML; WAI-ARIA; and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Competencies; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
What I Learned
The subject matter was a “tongue-and-cheek” approach with explaining metro culture to first-time visitors. Topics included escalator culture (walk on the left, stand on the right) and the pay stations with the world’s worse interface. In testing the website, my favorite tool was Web Disability Tester where I could experience the webpage as a user with that disability. In creating the website, I learned to have the skip to main content feature so the screen reader doesn’t read everything on the page. The biggest surprise was the emphasis on color contrast for low vision users. I found the color contrast tools very helpful in creating pages from WebAIM. In this class, I updated my HTML skills while learning how to use CSS for the first time. I found accommodating a website for disabilities not to be difficult and necessary for an inclusive user experience.
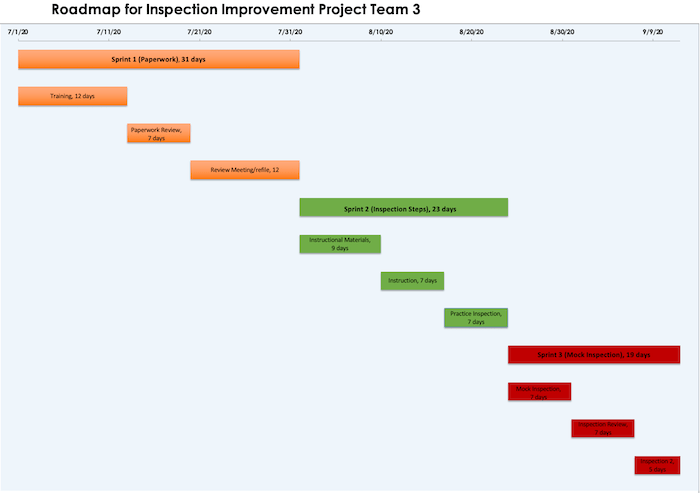
EDIT 573 AGILE
Teams will develop a plan for managing an instructional design project using Agile methods. Team members will decide collaboratively what instructional design project will serve as the basis of the team’s project plan. The final product must contain a rationale, instructional product vision statement, and a roadmap.
Keywords: AGILE; Collaborative Learning; and Project Management.
IBSTPI Competencies: Professional Competencies; Planning and Analysis; Design and Development; and Management.
Click on picture for a link to artifact.
What I Learned
AGILE has a lot of flexibility in its design. I like the testing of the product at the end of each sprint. In design thinking, the testing is done at the end in which failure leads back a few steps. Our team divided roles and provided feedback in this plan. My role became making the roadmap, a visual aid showing each sprint through the process. In the end, I used a Gaant Chart with detailed descriptions in a table below the chart. The roadmap provided a great visual aid to understanding the different aspects of the product. I liked the Gaant Chart with the detailed table over the suggested roadmap with just the sprints listed. Furthermore, I liked showing in the Gaant Chart the entire sprint with subsequent parts broken-down underneath.


